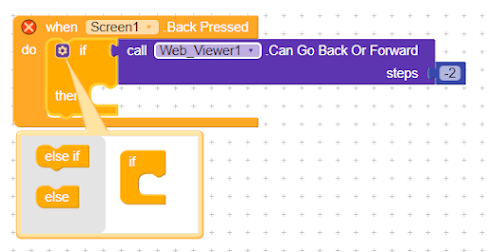
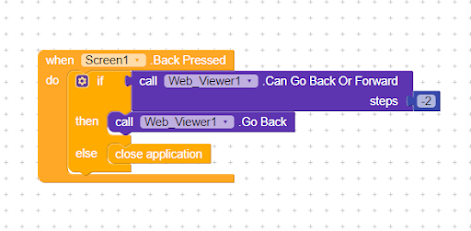
How to convert glide app to an android apk
Step1:
Login to https://www.kodular.io/
Step 2:
Click on CREATE APPS. Sign up your account. Now you will see the below screen. click create project and proceed.
Step 3:
Step 4:
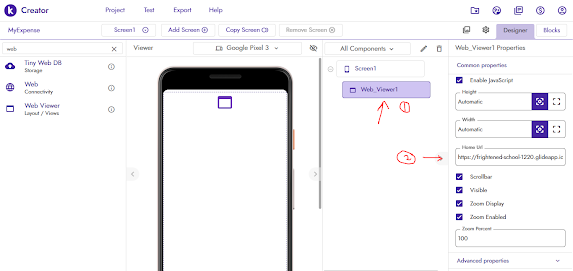
Click on the Web_Viewer1 component highlighted as 1 in the below image.
Properties pane opens at the right side, Give your glide url in the Home Url as highlighted in the below image as 2
Step 5:
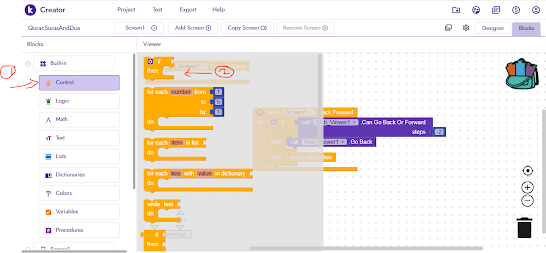
As highlighted in the below image click on the "Blocks" tab in the top right corner